Hydraulic hose

Figure 1: Hydraulic hose
Hydraulic systems require the movement of hydraulic fluid between components, which is done by the use of hydraulic hoses. These hoses are relatively stiff and often have several reinforcement layers. This article covers the components of a hydraulic hose, how to select the proper hydraulic hose for your application and typical applications.
Table of Contents
Tameson Hydraulic Hose Selection
Hydraulic hose components
A hydraulic hose is specifically designed for hydraulic systems. They convey high-pressure oils or water between the fluid ports of the pumps and actuators, where the oils or water are used to create mechanical movement. They are made up of three different layers: a core or inner tube (Figure 2 labeled C), a reinforcement layer or inlays (Figure 2 labeled B), and an outer cover (Figure 2 labeled A). The inner layer comes in direct contact with the fluid. So, they need to be chemically compatible with the fluid. The reinforcement layer is made up of steel, copper, or textile of high tensile strength. This layer provides the necessary strength to the inner tube and facilitates high-pressure applications. The reinforcements can have a helical, spiral, or braided design. The outer cover of the hose acts as a protective layer and should be compatible with the operating environment.
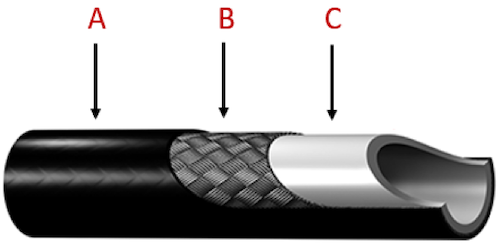
Figure 2: Hydraulic hose components: outer cover (A), reinforcement (B), & the core (C)
The hydraulic hose is used to convey the hydraulic fluid, which provides power to the machinery to perform its work. The hydraulic fluid also protects the machine components.
The different types of hydraulic fluids are mentioned below:
- Petroleum-based fluid: Protects from wear and tear, oxidation, corrosion, and extreme pressure.
- Water-based fluid: Used for fire-resistance because of its high-water content.
- Synthetic-based fluid: Provides fire-resistance, low-friction, thermal stability and is suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
Selection criteria
The following selection criteria should be considered before selecting the hydraulic hose for your application:
- Material: The material of the hydraulic hose should have chemical compatibility with the hydraulic fluid coming in contact with it. The hose is generally made up of synthetic rubber, like NBR (nitrile), EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer), and SBR (styrene-butadiene rubber). However, they can also be thermoplastics, Teflon, or silicone. Synthetic rubber hoses are suitable to use with hydraulic oils.
- Pressure: The hydraulic hose must be able to withstand the maximum working pressure, including pressure spikes that may occur during the operation.
- Temperature: The hydraulic hose should be able to work comfortably in a defined temperature range. Exposure to high temperatures for a long time can cause the hose to lose its flexibility. A high-temperature hydraulic hose should be used for such applications.
- Length: The hose length should be enough to allow for bending and flexing during the movement of the machinery parts.
- Diameter:The inside diameter of the hose should be compatible with the fluid flow rate for the application. The smaller the diameter, the higher the velocity. This high velocity will cause excess heat, friction, and turbulence in the system.
- Bending radius: A bending radius is a minimum radius that a looped hose can achieve without causing any damage to the hose. Bending should not occur at the start of the hose end fitting because this might result in leaks at the hose fitting. Tight bends can increase the turbulence of the hydraulic fluid which can damage the inner layer of the hose.
- Reinforcement: The reinforcements can be helical, spiral, or braided design. Helical design is best for suction application and spiral design for extreme high-pressure applications. A braided design is best used for a low or moderately high-pressure application.
- End connection: Depending upon your requirement, hydraulic hoses are available with pre-made fittings for fast and easy connection, or without fittings for easy customization according to your application. For pre-made fittings, it is important to ensure the correct size fittings for compatibility with your system.
- Accessories: The hoses need to be equipped with specialized hydraulic accessories to make sure they can fit on the pumps/actuators. Hydraulic hose clamps and hydraulic hose crimpers are used to ensure the hose is properly connected to the fittings and are crimped to the exact diameter. The fittings used should be specifically designed for the hydraulic application, with the ability to withstand high pressure. A hydraulic hose cutter can be used to ensure the perfect length of the hose for the application.
Common applications
Some common applications where hydraulic hoses are used:
- Construction equipment like excavators, dump trucks, loaders, bulldozers, pavers, etc.
- Agricultural equipment like trucks, harvesters, fertilizer, manure spreaders, etc.
- Snow and ice removal equipment
- Mining equipment like excavators, miners, drills, etc.
- Factory applications like assembly lines, presses, robotics, hydraulic power units, etc.
FAQs
What are hydraulic hoses used for?
Hydraulic hoses are primarily used to allow the flow of hydraulic fluid between different components in a hydraulic system.
How often should hydraulic hoses be replaced?
For preventive maintenance, the hydraulic hose should be replaced every year or two, depending on how the machine is used. However, regular inspection is required to prevent failure.
How do I choose a hydraulic hose?
When choosing a hydraulic hose, hydraulic hose sizes like length and diameter should be given careful consideration. Temperature and pressure range, hydraulic hose material, the fitting requirement should also be considered.





