When To Clean and Replace Pneumatic Filters

Figure 1: Pneumatic filter
Regular air compressor filter replacement is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of pneumatic systems. In industries like food and beverage processing or pharmaceuticals, where product quality hinges on compressed air purity, regular filter maintenance is essential. Clean filters prevent contamination, ensure efficient energy use by maintaining optimal air pressure, and help avoid costly downtime by reducing the risk of unexpected equipment failures. This article explores the role of filters for air compressors, provides guidance on when to change them, and offers a detailed guide to cleaning an air compressor filter.
Table of contents
- Understanding the role of pneumatic filters
- When to change pneumatic filters
- How to maintain and clean pneumatic filters
- FAQ
View our online selection of pneumatic filters!
Understanding the role of pneumatic filters
A pneumatic filter removes contaminants like dirt, dust, and moisture from a compressed air system. This filtration is crucial because these contaminants can damage pneumatic components and decrease the system's efficiency. Pneumatic filters can be singular units or part of a more complex unit, such as a filter, regulator, lubricator (FRL) unit. They are typically located close to the point of use of the compressed air. The contaminants in a compressed air system can originate from various sources:
- Ambient air intake: Dust, pollen, and other airborne particles can enter the system through the air intake.
- Compressor residues: Oil and other residues from the compressor can contaminate the air.
- Air distribution hoses or pipework: Rust, scale, and other debris can accumulate in the distribution network.
- Air receiver: Moisture and other impurities can collect in the air receiver.
The primary contaminants include water (in various forms), oil, dirt, and micro-organisms. While most filters can effectively remove water, oil, and dirt, specialized filters are required to eliminate microorganisms, especially in sensitive industries like food and pharmaceuticals.
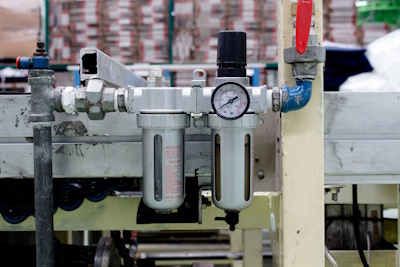
Figure 2: An air filter used in a pneumatic system
When to change pneumatic filters
Some indicators that it is time to replace an air compressor filter are:
- Age and wear: Replace filters if they are old or show signs of wear, such as rust or caked-on dirt.
- Scheduled maintenance: It is recommended to change an air compressor filter twice a year. For rotary screw compressors, replace air and oil filters every 2,000 hours and separators every 8,000 hours. Always check the manufacturer's guidelines for specific recommendations.
- Pressure drop: Clogged filters restrict airflow, causing pressure drop. Regularly monitor the pressure differential across the filter; a significant increase indicates the filter is not performing well and needs replacement.
- Visual inspection: Check for excessive dirt, oil buildup, or damage to the filter media. Replace the filter if it appears dirty or damaged. Even if it looks clean, adhere to the manufacturer's replacement schedule, as some contaminants might not be visible.
- Changes in air quality: A sudden drop in compressed air quality suggests the filter may be failing. Increased moisture, oil, or particulates in the air supply indicate inadequate contaminant removal. This can cause equipment damage, product spoilage, and higher operational costs.
- Increased energy consumption: A clogged filter makes the compressor work harder, increasing energy consumption. If energy bills rise without increased production, check the pneumatic filter. Replacing a clogged filter can boost system efficiency and lower energy costs.
How to maintain and clean pneumatic filters
Regular inspection and cleaning are key to maintaining any air filtration system. Refer to the instruction guide or owner's manual for specific cleaning instructions for the compressed air filter. Follow these general steps to clean a pneumatic filter:
- Turn off the air compressor and allow it to cool before handling.
- Once cooled, unscrew and remove the protection cage and top cover from the filter base.
- Inspect the protection cage and top cover for any signs of damage or issues that might be concerning.
- Remove the filter bowl and inspect it for any problems or accumulated debris.
- Take out the filter element and inspect it for any signs of wear or damage. Many industrial filter elements can be cleaned and reused. It is important to verify whether the filter elements are the type that can be cleaned. For example, coalescing filter elements, high-efficiency filter elements, and filters with special filtration media typically cannot be cleaned.
- Filter cleaning by hand: Remove the cartridge filter from its housing and hold it upright with one hand. With the other hand, gently move across the fins in a strumming motion. This light snapping action will dislodge most of the dirt. The filter cartridge is then ready for use.
- Filter cleaning by compressed air: Use about 7 bar (100 psi) of air pressure to clean the filter element. First, blow air through the inside of the filter, focusing on the internal surfaces to dislodge dirt. Then, blow air over the outside of the filter, directing it downward to avoid pushing dirt deeper into the material. Finally, blow air through the inside once more to ensure any remaining dirt is removed from the clean side of the filter.
- Filter cleaning by washing: After cleaning the filter element with compressed air, restore it by washing or soaking in soapy water. Rinse and remove excess moisture with compressed air. Avoid drying with heat or using solvents like gasoline or alcohol, as these can damage the plastic end seals.
- Check the condensate drain valve for proper operation and clear any blockages.
- If the air compressor filter does not need replacement, reassemble the components by securing the filter element, filter bowl, protection cage, and top cover back in their original positions.
- Ensure the condensate drain valve is functioning correctly before reattaching the cover.
Clean the pneumatic filter ideally every month, but at least once per season, to ensure optimal performance. The type of filter material (e.g., paper, synthetic, or metal) can affect the cleaning frequency and air compressor filter replacement schedule. For example:
- Paper filters are typically disposable and require regular replacement.
- Synthetic filters can often be cleaned and reused, extending their lifespan.
- Metal filters are durable, allowing for repeated cleaning, but may require more effort to maintain.
If air quality or performance remains poor after cleaning, it may be time to replace the pneumatic filter.
FAQ
Can a clogged oil filter affect air compressor performance?
Yes, it can reduce efficiency, increase wear, and potentially cause overheating or damage.





