What Is a Ball Check Valve

Figure 1: Ball check valve made of nickel-plated brass
A ball check valve lets fluid flow in only one direction by using a ball to block reverse flow. This design prevents backflow that could damage pumps, contaminate water, or cause system pressure loss. Ball check valves are well-suited for viscous media, and are typically available in smaller sizes (up to ⅜ inches/9.5 mm). They are durable and require minimal maintenance, with gravity-operated versions needing even less maintenance because they do not have a spring.
View our online selection of check valves!
How does a ball check valve work
A ball style check valve uses a spherical ball that seals against a seat with an orifice smaller than the ball diameter to prevent backflow.
- Normal flow: When upstream pressure exceeds the cracking pressure, the ball lifts from the seat, allowing fluid to pass.
- Backflow prevention: If downstream pressure exceeds upstream pressure, or flow reverses, the ball returns to the seat to form a seal.
Ball check valve design
Gravity-operated (without spring)
The ball moves freely under fluid pressure. If the valve is vertically installed, gravity returns the ball to the seat when flow stops.
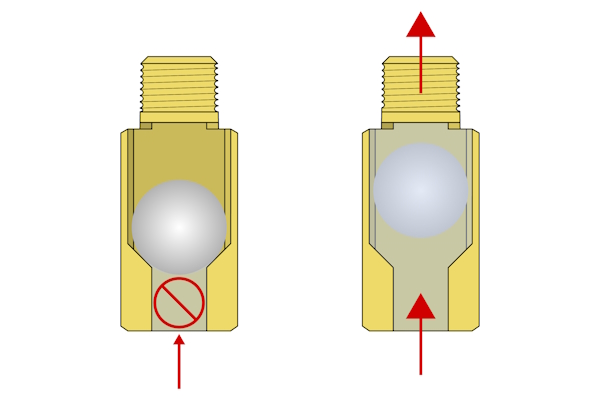
Figure 2: A ball check valve without a spring: When the valve is vertically installed, the ball lifts to pass the fluid upward (left). When the flow stops, gravity causes the ball to fall back into its seat.
Spring-loaded
A spring helps the valve close, enabling faster sealing and reliable operation regardless of valve orientation.
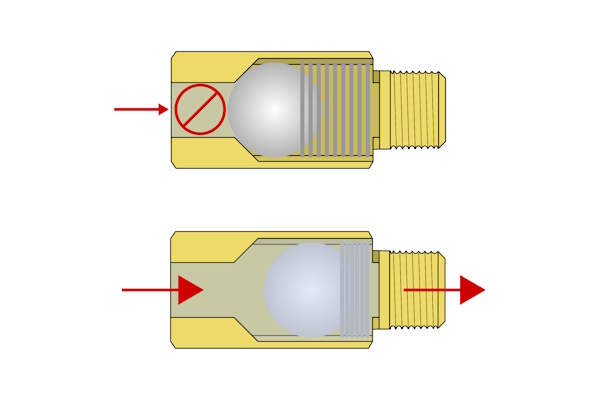
Figure 3: Spring-loaded ball check valve diagram: closed position preventing backflow (A) and open position allowing flow (B).
How to select the right ball check valve
End connection
The end connections attach the valve to the piping system. Ball check valves with threaded ends are easy to install and often used in smaller piping systems.
Material
Ensure the ball check valve materials are compatible with the system's media, temperature, and pressure.
- Body: Brass offers excellent strength and durability for many applications. It is often plated with nickel to provide superior protection against atmospheric corrosion.
- Ball and spring: The spring and ball made of stainless steel are highly durable and can withstand frequent operations.
-
Seals:
- FKM: Provides excellent compatibility with process chemicals and solvents up to 130 °C/266 °F. FKM seals are ideal for hot fluids, aggressive media, or oils in HVAC, chemical processing, and high-temperature industrial lines.
- NBR: Offers good resistance to water, air, and most oils up to 90 𐩑C/194 𐩑F. They are used in general-purpose plumbing, pneumatic, and low-temperature hydraulic systems.
Read our chemical compatibility chart for more details on the suitability of these materials for specific media and operating conditions.
Speed of operation
Ball check valves with a spring are fast. They are ideal for systems where the flow changes quickly or where precise control is needed. However, they require more maintenance due to spring fatigue.
Installation orientation
Spring-loaded ball check valves can be installed horizontally or vertically. Gravity-operated ball check valves must be installed vertically with flow directed upward. Gravity returns the ball to the seat when the flow stops or reverses.
Ball check valve maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures ball check valves perform consistently and achieve maximum service life. The following guidelines will help maintain optimal operation and assist in identifying potential issues early:
- Remove debris regularly to prevent ball obstruction and loss of function.
- Inspect ball and seat for wear, pitting, or corrosion; replace if damaged.
- Check alignment so the flow direction arrow matches the system flow.
- Lubricate if required using only manufacturer-approved products.
- Monitor noise/vibration as early signs of blockage or misalignment.
- Inspect spring (if fitted) for fatigue, corrosion, or breakage.
- Test for leaks/backflow with visual checks or pressure tests.
FAQs
What does a ball check valve do?
A ball check valve allows fluid to flow in one direction and prevents backflow. It uses a ball that seals against a seat.
Can a ball check valve be installed horizontally?
Spring-operated ball check valves can be installed horizontally or vertically. Gravity-assisted ball check valves should be installed vertically.
Is a ball valve and a ball check valve the same?
A ball valve is used to control the flow of a fluid by rotating a ball with a hole through it. A ball check valve allows fluid to flow in only one direction. It uses a ball to block reverse flow.






