Single Acting vs Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder

Figure 1: Round pneumatic cylinders: single-acting (left) and double-acting (right)
Single-acting and double-acting pneumatic cylinders are two of the most common actuators used in industrial applications. Choosing between these cylinder types depends on several factors, including the required force and motion and the specific application requirements. This article explores the key differences between single-acting and double-acting pneumatic cylinders and discusses their advantages, disadvantages, and application-specific suitability.
Table of contents
- Pneumatic cylinder operating principle
- Single-acting pneumatic cylinders
- Double-acting pneumatic cylinder
- Choosing the right pneumatic cylinder
- FAQs
View our online selection of pneumatic cylinders!
Pneumatic cylinder operating principle
A pneumatic cylinder converts compressed air energy into linear motion. When compressed air is supplied to one end of the cylinder, the pressure pushes the piston or rod, which performs the mechanical work. A valve regulates compressed air flow into and out of the cylinder, which controls the piston or rod's movement. The efficiency and accuracy of the cylinder's operation depend on the piston and cylinder's size, shape, and material, as well as the pressure and flow rate of the compressed air. Learn more about how pneumatic cylinders operate by reading our pneumatic cylinder overview.
Single-acting pneumatic cylinders
A single-acting pneumatic cylinder operates in one direction. Compressed air enters one side and pushes the piston to the other side. When the air supply shuts off, a spring (Figure 2) or an external force returns the piston to its original position.
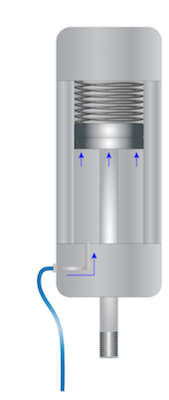
Figure 2: A single-acting pneumatic cylinder's working principle: compressed air pushes the piston in one direction, and a compressed spring returns the piston to its original position.
Advantages and disadvantages
Single-acting pneumatic cylinders have the following advantages and disadvantages:
-
Advantages
- Cost: Single-acting cylinders are the cost-effective solution for applications that only require one direction of movement.
- Air pressure: These cylinders require less air pressure than double-acting pneumatic cylinders.
- Fail safe: If air pressure is lost due to a malfunction, the spring in the cylinder will automatically return the piston to its original position.
-
Disadvantages
- Control: Although single-acting pneumatic cylinders technically work in both directions, they do not offer the level of control and precision that double-acting cylinders do.
- Spring issues: The spring mechanism in a single-acting pneumatic cylinder can be prone to failure and it takes up potential work area space.
Applications
- Clamping: Single-acting cylinders are used for clamping applications, where a part or component is held in place. For example, in the woodworking industry, single-acting cylinders hold wood pieces in place while they are being cut or drilled.
- Ejection: In the plastics industry, single-acting cylinders eject finished parts from molds. The compressed air pushes the piston, pushing the finished part out of the mold.
- Lifting: Single-acting pneumatic cylinders can be used for lifting tasks, such as air-powered lifts or vehicle jacks. When compressed air is supplied, it drives the piston upwards, raising the load, and a spring or other external force brings the piston back down to its initial position.
Double-acting pneumatic cylinder
A double-acting pneumatic cylinder operates in both directions, with compressed air applied to both sides of the piston, creating a force in either direction. The air supply pressure to one port pushes the piston towards one side of the cylinder, and reversing the air supply to the other port pushes the piston back to the other side (Figure 3). A 5/3-way pneumatic solenoid valve controls the airflow to each port to move the piston fully in both directions and hold it at an intermediary position.
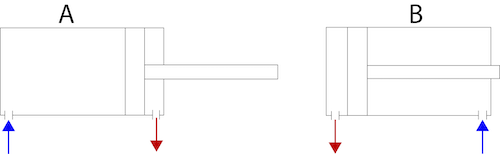
Figure 3: The working principle of a double-acting pneumatic cylinder. The blue arrows represent the ports receiving the compressed air, pushing the piston away from the port.
Advantages and disadvantages
One of the main advantages of double-acting pneumatic cylinders is their ability to provide a precise and controlled motion in both directions. They are also typically more reliable than single-acting cylinders, as they do not rely on a spring return mechanism. However, double-acting cylinders require more compressed air than single-acting cylinders, and they can be more expensive.
Applications
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders are used in various industrial applications where precise control of motion and force is required. Some common applications include:
- Material Handling: Double-acting cylinders are used in material handling applications, such as conveyor systems or lifting equipment. They provide more precise control of motion and force, allowing for efficient and safe handling of materials.
- Robotics: Double-acting cylinders are commonly used in robotics, where precise and controlled motion is essential. They control the movement of robot arms and other components.
- Machine Tools: Double-acting cylinders are used in machine tools, such as milling machines or lathes. They control cutting tools and other components precisely, allowing for efficient and accurate machining.
Choosing the right pneumatic cylinder
Despite using compressed air as their power source, single-acting and double-acting pneumatic cylinders have distinct performance characteristics due to their different port designs. Single-acting cylinders are mainly used in industrial settings that require force in one direction, such as ejecting parts from conveyor belts. However, double-acting cylinders have superior speed, strength, and efficiency, making them well-suited for applications that demand high force and rapid movement. In summary, single-acting cylinders are suitable for light assembly work. Double-acting cylinders are better suited for applications requiring both speed and force.
FAQs
Which are better, single- or double-acting pneumatic cylinders?
The better choice between single- and double-acting pneumatic cylinders depends on the application. For example, single-acting is more suitable for simple applications that do not require controlled retraction.
What is the difference between single-acting and double-acting pneumatic cylinders?
Single-acting cylinders have one entry port for compressed air, pushing the piston in one direction. Double-acting cylinders have an entry port on each end, allowing the air to control the piston in both directions.











