Festo Semi-rotary Drives

Figure 1: A vane semi-rotary drive (left) and rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drive (right).
Semi-rotary drives provide precise and controlled limited rotational movement in various industrial applications, typically less than 360 degrees. These drives are commonly used in applications where a full rotation is not necessary or possible. They are often used in various industrial applications, including valve actuation, material handling, and automation systems. This article uses Festo's pneumatic semi-rotary drives as an example to provide an overview of this device type.
Festo offers two primary types of pneumatic semi-rotary drives:
- Vane semi-rotary drive
- Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drive
Vane semi-rotary drive
A vane semi-rotary drive uses a vane (a flat, blade-like component) that rotates within a chamber. The vane is attached to a rotor, and as pressurized air is introduced into the chamber, it pushes against the vane, causing the rotor to turn. Festo's double-acting (meaning it can turn in two directions) semi-rotary drives with a vane are modern, compact devices that offer a fixed swivel angle, which can be adjusted using accessories. It is lighter than other semi-rotary drives and features a housing that is protected against splash water and dust. The design does not include a metal fixed stop, making it smoother and quieter.
These devices incorporate position sensors like the SRBS, which magnetically and without contact detect when the drive has reached the end of its turning range. This sensor features two switching points and has quick installation and reliable operation via a single push button. The end positions of the swivel angle, ranging from 0 to 270 degrees, can be easily set with this button. The SRBS sensor requires only one connecting cable and offers a long service life due to its robust, non-contact sensing mechanism. It provides a repetition accuracy of ±1 degree and includes programmable switching outputs, either PNP or NPN, with options for normally open or normally closed contacts.
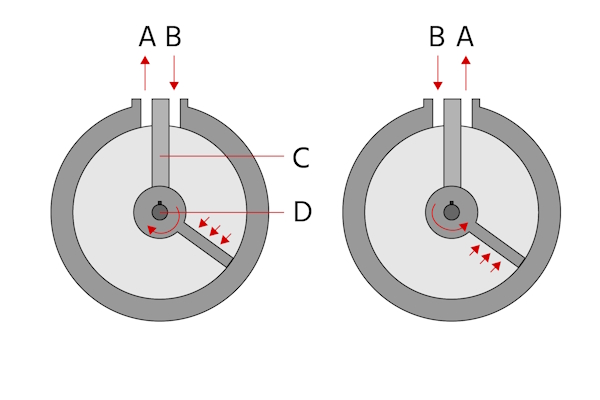
Figure 2: Vane type semi-rotary drives have ports for return flow (A) and compressed air flow from a pump (B). Alternating which port is for which source can change the direction the vane is pushed (clockwise left, counterclockwise right). The stopper (C) separates the two ports and the vane rotation rotates an output shaft (D).
Specifications
Festo offers two series of vane semi-rotary drives:
- DRVS
- DSM
The DSM drive offers larger sizes and also allows for higher radial forces from the load. The primary difference between the two series, however, is that the DSM swivel angle is infinitely adjustable and the DRVS swivel angle is fixed. However, the DRVS swivel angle can be adjusted using a stop kit accessory.
Table 1: DRVS specifications
Size |
6 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 25 | 32 | 40 | |
Pneumatic connection |
M3 |
M5 |
G1/8 |
|||||
Mounting type |
Female |
|||||||
Swivel angle |
90/180 |
90/180/270 |
||||||
Lubrication |
Possible but will always be required afterwards |
|||||||
Operating pressure |
bar | 3.5 - 8 |
2.5 - 8 |
2 - 8 |
||||
| psi | 51 - 116 |
36 - 116 |
29 - 116 |
|||||
Materials | ||||||||
Drive shaft |
High-alloy stainless steel |
Nickel-plated steel |
||||||
Housing |
Anodised wrought aluminum alloy |
Painted die cast aluminum |
||||||
Vane |
Reinforced PET |
|||||||
Ball bearings |
Roller bearing steel |
|||||||
Shaft seal |
- |
PU |
NBR | |||||
Screws |
Galvanized steel |
|||||||
Seals |
TPE-U(PU) |
|||||||
Table 2: DSM specifications
| Size | 12 | 16 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 63 |
| Pneumatic connection | M5 |
G1/8 |
G1/4 | |||
| Mounting type | Female thread |
|||||
| Operating pressure (bar) | 2 - 10 |
1.5 to 10 |
||||
Materials | ||||||
| Housing, flange | Anodised aluminum |
|||||
| Shaft | Nickel-plated steel |
|||||
| Rotary vane | Glass fiber-reinforced plastic |
|||||
| Stop lever | Anodised aluminum |
|||||
| Fixed stops | Stainless steel |
|||||
| Screws | Galvanized steel |
|||||
| Stop screws | Stainless steel |
|||||
| Cover cap | Glass fiber-reinforced plastic |
|||||
| Seals | Polyurethane |
|||||
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drive
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives operate on the rack and pinion principle, offering high accuracy in end positions and excellent load-bearing capacity. They convert linear motion into rotational motion through the interaction of a gear (the pinion) and the linear gear strip (the rack). Compressed air applies a linear force to the rack, causing it to move in a straight line. This leads to the pinion rotating around its axis. These drives maintain precise alignment along the axis of the flange shaft, minimizing any deviation or wobble. Additionally, they are capable of effectively managing and controlling large rotational forces, which are referred to as high mass moments of inertia. They feature low backlash (jerky movements when direction is changed) and provide a good dynamic response. Designed to be splash-proof to IP65 standards based on EN 60529, these drives come with defined interfaces and a supply port at one end. Various mounting options are available, making them ideal for handling applications.
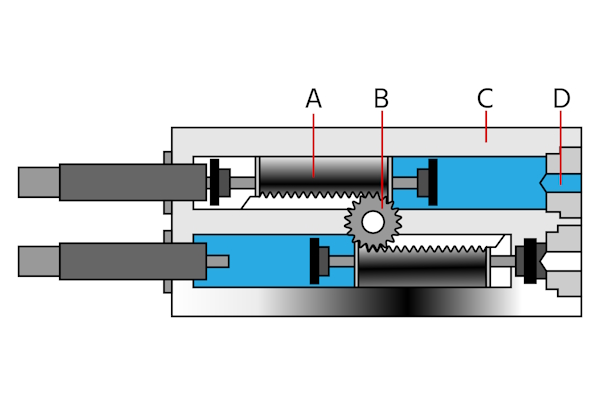
Figure 3: A rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drive: pistons (A), flange shaft (B), housing (C), and port plugs (D).
Specifications
Festo offers one series of rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives, the DRRD series with twin pistons. Its specifications are seen in Table 3.
Table 3: DRRD specifications
| Size | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Pneumatic connection | M3 |
M5 | |
| Mounting type | Female thread with through-hole |
||
| Swivel angle | 180 |
||
| Lubrication | Permissible but will always be required afterwards |
||
| Operating pressure (bar) | 3 to 8 |
||
Materials | |||
| Piston | Copper base alloy |
||
| Flange shaft | High-alloy stainless steel |
||
| Housing | Smooth-anodised wrought aluminum alloy |
||
| Port plug | High-alloy stainless steel |
||
| Seals | NBR |
||
| Piston seal | TPE-U(PU) |
||
Applications
This section provides guidance on how to select between a vane semi-rotary drive and rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drive for specific applications.
Precision and smoothness of operation
Vane semi-rotary drives are known for their smooth and precise rotational movement, making them ideal for applications requiring fine control and minimal vibration. These drives are particularly suitable for delicate tasks in automation, robotics, and medical equipment where precision is critical.
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives provide robust and reliable rotational movement but may have slightly more mechanical play compared to vane drives. They are suitable for applications where high precision is not as critical, such as heavy machinery and automotive steering systems.
Torque and load capacity
Vane semi-rotary drives typically offer moderate torque and are best suited for applications with lighter loads. They are ideal for packaging machines, labeling systems, and light-duty material handling.
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives are capable of delivering higher torque and handling heavier loads. These drives are more robust and durable under high-stress conditions, making them suitable for heavy machinery, cranes, excavators, and other applications requiring high torque.
Space and installation constraints
Vane semi-rotary drives are generally more compact and easier to install in confined spaces. Their design allows for integration into tight areas, making them ideal for applications with limited space, such as robotic arms and compact automation systems.
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives, however, may require more space due to the linear-to-rotary motion conversion mechanism. Despite this, they offer flexibility in mounting and configuration, making them suitable for larger installations where space is less of a concern, such as industrial machinery and renewable energy systems.
Maintenance and durability
Vane semi-rotary drives typically have fewer moving parts, which can result in lower maintenance requirements and longer service life in clean environments. They are best for environments where maintenance access is limited, such as medical devices and aerospace applications.
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives are known for their robustness and ability to withstand harsh conditions. While they may require more maintenance due to the mechanical components, they are generally more durable in rugged environments. These drives are ideal for outdoor applications, heavy industry, and environments with high levels of dust and debris.
Cost considerations
Vane semi-rotary drives may be more cost-effective for applications requiring moderate torque and precision. The simpler design can lead to lower initial costs, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects where high precision and moderate torque are sufficient.
Rack-and-pinion semi-rotary drives, on the other hand, may have higher initial costs due to their robust design and higher torque capabilities. However, they offer better value for applications requiring high performance and durability. These drives are suitable for projects where long-term reliability and high torque justify the investment.
FAQs
What is a semi-rotary drive?
A semi-rotary drive provides precise and controlled limited rotational movement, typically less than 360 degrees, used in various industrial applications.
What are Festo semi-rotary drives used for?
Festo semi-rotary drives are used for valve actuation, material handling, and automation systems where full rotation is not necessary.
What are the benefits of using Festo semi-rotary drives?
Benefits include precise control, reliability, compact design, and suitability for various industrial applications requiring limited rotational movement.



