Digital vs Analog Input/Output (I/O) modules
Figure 1: An analog I/O module (left) and a digital I/O module (right).
I/O modules allow for timely and accurate exchange of information between control systems (e.g., PLC) and field devices (e.g., sensors and actuators). An I/O module, or Input/Output module, converts physical signals from field devices into a digital format that a control system can process and vice versa. There are two main types of I/O modules: analog and digital. Each type has specific applications and advantages, which this article explores in detail.
Table of contents
- Analog I/O modules
- Digital I/O modules
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Selecting the right I/O module for an application
View our online selection of modules!
Analog I/O modules
Analog signals (Figure 2 labeled A) are continuous signals that vary over time and can take on any value within a given range. Unlike digital signals (Figure 2 labeled B), which are discrete and binary, analog signals represent information in a form that is directly proportional to the physical quantity being measured.
In industrial applications, analog signals represent temperature, pressure, flow rate, and level parameters. These signals are typically measured in volts (V) or milliamps (mA). For instance, a temperature sensor might output a voltage that varies continuously with the temperature, or a flow meter might produce a current signal proportional to the flow rate. Analog I/O modules handle these continuous signals, converting them into digital data that the control system can process. This conversion is essential for accurate monitoring and control of industrial processes.
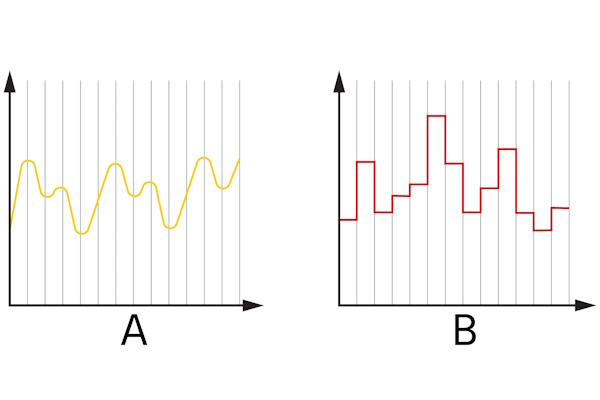
Figure 2: Analog signals (A) have values along a continuous range and digital signals (B) have discrete values along a range.
Analog I/O module applications
Analog I/O modules are widely used in various industrial applications. Some common applications include:
- Sensor data acquisition: Analog I/O modules collect data from sensors like temperature, pressure, and flow meters. These sensors give continuous signals that are converted into digital data for the control system to process and analyze.
- Temperature control: Analog I/O modules get continuous signals from temperature sensors (like thermocouples or RTDs) and send these data to the control system. The system then makes real-time adjustments to keep the desired temperature.
- Pressure measurement: Pressure sensors send continuous signals that show pressure levels. These signals are converted by the analog I/O module and used by the control system to keep pressure within safe and optimal ranges.
Digital I/O modules
Digital signals are binary in nature, meaning they can only take on one of two possible states: on or off, represented numerically as 1 or 0. This binary representation makes digital signals discrete, instead of the continuous nature of analog signals.
In industrial applications, digital signals represent simple, clear-cut conditions such as the presence or absence of an object, the open or closed state of a valve, or the on or off status of a motor. These signals are easy to process and interpret by control systems, which can quickly make decisions based on the binary input. Digital I/O modules are designed to handle these binary signals, converting them into a format that the control system can use for monitoring and control purposes.
Digital I/O module applications
Some typical digital I/O module applications include:
- Switch status monitoring: Digital I/O modules monitor limit switches, push buttons, and toggle switches. These switches give on/off signals to show if a condition is met, such as a machine part's position or a safety mechanism's activation.
- Relay controls: Digital I/O modules control relays to switch electrical circuits on and off. This is crucial for managing devices like motors, lights, and heaters. By sending a digital signal to the relay, the control system can control these devices.
- Simple on/off signals: Many industrial processes need to control devices that work in a simple on/off way. Digital I/O modules are perfect for this, as they send and receive binary signals to control devices like solenoid valves, alarms, and indicator lights.
Advantages and disadvantages
Table 1 overviews the advantages and disadvantages of digital vs analog input
Table 1: The advantages and disadvantages of analog and digital I/O modules
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Analog I/O Module | Handles continuous signals for precise measurement and control Represents smooth and continuous variations |
More complex to set up; requires accurate calibration and signal conditioning More susceptible to electrical noise and interference; requires shielding and filtering |
| Digital I/O Module | Easier setup and configuration; binary nature simplifies wiring and reduces errors More resistant to electrical noise and interference |
Can only handle binary signals; limited in representing complex, real-world signals Less precision in representing varying quantities |
Selecting the right I/O module for an application
When choosing between analog and digital I/O modules, consider several factors to ensure the right fit for an application:
- Type of signal: Decide if the application needs continuous signals (analog) or binary signals (digital). Use analog I/O modules to change temperature, pressure, and flow rate values. Use digital I/O modules for simple on/off states, like checking switch status and controlling relays.
- Required precision: Check how precise the application needs to be. Analog I/O modules give high precision and are good for tasks needing detailed measurement and fine control. Digital I/O modules are less precise but work well for tasks that do not need detailed data and can use simple on/off decisions.
- Environmental conditions: Think about the environment where the I/O modules will work. Analog signals can be affected by noise and interference, so they need extra protection like shielding and filtering. Digital signals are stronger in noisy places, so digital I/O modules are better in areas with high electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Cost: Look at the costs of each type of I/O module. Analog I/O modules can be more expensive because they need precise calibration, signal conditioning, and noise protection. Digital I/O modules are usually cheaper, easier to set up, and less affected by noise.
FAQs
What is the difference between digital and analog input?
Digital input reads discrete signals, while analog input reads continuous signals, allowing for more detailed data representation.
What is an analog I/O module?
An analog I/O module processes continuous signals, converting them to digital for control systems or vice versa for field devices.
What is a digital I/O module?
A digital I/O module processes discrete signals, enabling on/off control and status monitoring in control systems.







