Guide to Using Float Switches in Water Tanks

Figure 1: A tethered float switch for water tank
Float switches in water tanks can be used to notify a pump that the water level is low and water can be pumped into the tank, water level is high enough that no water should go into the tank to prevent overflow, or to open valves to drain the tank. A float switch detects if the water level in a tank is too high or low and controls devices like pumps (by turning them on or off), valves (by opening or closing them), or alarms to notify users. Float switches are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to ensure efficient and reliable operation of water storage systems. This article explores the different types of float switches for water tanks and their selection criteria.
Table of contents
- Float switch in a water tank
- Applications
- Selecting the right float switch for a water tank
- Additional components
- Working
- FAQs
View our online selection of float switches!
Float switch in a water tank
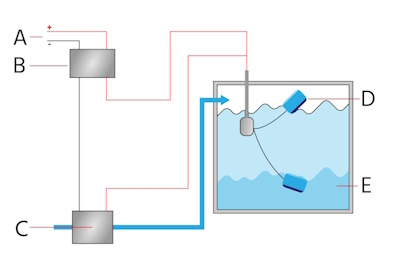
Figure 2: Float switch for a water tank: Power supply (A), relay(B), pump (C), float (D), and water tank (E). When the water level is high, the floating ball rises and the pump stops working. When the water level is low, the floating ball sinks, turning the pump on.
Float switches monitor water levels in the tank and provide real-time information, whether the tank is full, empty, or at a specific level. They help maintain a consistent water level by opening valves to allow water in when it drops below a specific point and closing them when the desired level is reached.
Tethered float switches are typically used for automated water level control in tanks, utilizing a flexible tether to detect water levels. The float, typically made from durable, buoyant materials like polyethylene, contains an internal tilt or mercury switch that activates based on the float's orientation. The tether length and tether point are crucial for determining the float's range of motion, while the switch mechanism changes state at a specific tilt angle, usually around 10-20 degrees. Read our float switch overview article for more information on the working and types of float switches.
Note: While there are various types of float switches available (like horizontal and vertical float switches), tethered float switches are the most commonly used for automated water level control in tanks.
Applications
Several industries use float shut-off switches in water tanks for various applications, some involving liquids other than water.
- Water department: Water towers have float switches, so personnel know the water levels and can stay prepared.
- Mining and extraction: Mining and extraction industries use sump pit float switches.
- Transportation: Liquid level switches in fuel tanks constantly monitor fuel levels. Float switches in coolant tanks constantly monitor coolant levels.
- Well: A float switch monitors water levels in a well to determine if there is enough for use.
- Cistern: A cistern has a float switch that controls filling after a flush.
- Water storage tanks: Float switches indicate when water flows into the storage tank should stop or start depending on the level.
Selecting the right float switch for a water tank
Choosing the optimal float point for a water tank involves several key considerations to ensure accurate and reliable water level control.
- Tank size and depth: Ensure the float switch has an appropriate stem or cable length to reach the desired water levels. The length of the tether determines the range of motion of the float. A longer tether allows for a greater range of water level detection but may introduce more variability in the switch activation point.
- Float switch model: Choose MAC3 float switch (Figure 3 left, middle) for residential or industrial settings with clean water and moderate turbulence, especially if ACS certification for drinking water is needed. Choose the MAC5 float switch (Figure 3 right) for environments with wastewater, high levels of grease, or suspended solids, and where ATEX certification and built-in counterweight stability are essential. Read our MAC3 vs MAC5 float switch article for more details.
- Determine the control range: Identify the minimum and maximum water levels that need to be maintained in the tank. This range will dictate the length of the tether and the positioning of the float switch.
- Switching action: Decide whether the application needs a normally open or normally closed switch. An NO switch is typically used to activate a pump when the water level drops, while an NC switch is used to deactivate a pump when the water level rises. A float switch with a changeover contact can be used for filling and emptying operations (NC or NO).
- Operating voltage and current: Ensure the float switch is rated for the voltage and load of the application and are compatible with the control circuit to prevent electrical issues and ensure safe operation.
-
Mounting options:
- Float position: Position the float switch away from any potential obstructions or areas of high turbulence to ensure accurate readings. The float should be able to move up and down smoothly with the water level.
- Tether point: Secure the tether (anchor) point at a fixed position within the tank to ensure the float can move freely without obstruction. The tether point should be placed in a location that avoids turbulence and direct water flow from inlets or outlets.
- Counter weight: Attach the counter weight to the cable at the appropriate position to set the desired control level. The counter weight helps stabilize the float and ensures it remains in the correct orientation. MAC5 float switches have built-in counterweights, whereas MAC3 float switches rely on external counterweights for stability.
- Liquid compatibility: Verify that the materials used in the float switch are compatible with water. Different liquids may require specific materials to prevent corrosion or degradation. Most water level indicators use stainless steel or plastic.
Read our float switch wiring article for more information on the float switch wiring diagram for water tanks.

Figure 3: MAC3 (left and middle) and MAC5 (right) float switches
Additional components
- Valves: Valves control the water flow into or out of the tank. A solenoid valve, connected to the float switch, can automatically open or close based on the water level, maintaining optimal levels without manual intervention. Learn more in our article on how to wire a float switch to a solenoid valve.
- Pipes and hoses:Pipes and hoses enable water transfer between the tank, valves, and other water system parts. The size and material of these components depend on the flow rate, pressure, and the application's specific requirements.
- Pump: The float switch can activate a pump to fill the tank when the water level drops below a certain point.
- Control panel: A control panel provides a centralized interface to monitor and manage the water tank system. It may include indicators, switches, and alarms to ensure optimal control and safety.
How does a water tank float switch work
When water levels change within the tank, the float switch moves accordingly, signaling the control panel or directly controlling other components.
Mechanism for filling water tank
- The float switch detects low water levels.
- The control system activates the solenoid valve.
- The solenoid valve opens to allow water into the tank.
- The float switch detects high water levels.
- The control system deactivates the solenoid valve.
- The solenoid valve closes to stop the water flow.
Water tank draining process
- The float switch detects high water levels.
- The control system activates the solenoid valve or pump.
- The solenoid valve opens, or the pump starts to drain water.
- The float switch detects low water levels.
- The control system deactivates the solenoid valve or stops the pump.
- The solenoid valve closes, or the pump stops, ending the draining process.
Note: The described process is just one way of managing water levels in a tank. There are various configurations and components that can be used depending on the specific application. For instance, instead of using a solenoid valve, the float switch could be directly connected to a pump to control water flow. Additionally, an electric ball valve might be used instead of a solenoid valve, depending on the requirements and design of the system.
FAQs
What is a float switch for a water tank?
A float switch monitors a water tank's level, opening and closing circuits to control devices like alarms and pumps, thereby managing the water supply.
How to get float switch alerts at different levels on a water tank?
Use a stem-mounted float switch. Several floats can be on a single stem. Some vertical float switches also activate switches at different levels.





