PVC Ball Valve - How They Work

Figure 1: Example of a double union PVC ball valve.
PVC (PolyVinyl Chloride) ball valves are widely used plastic shut off valves. The valve contains a rotary ball with a bore at the center. By rotating the ball a quarter-turn, the bore can be aligned inline or perpendicular to the piping to open or block the medias flow. PVC valves are durable, cost-effective, and used for a wide variety of media, including water, air, corrosive chemicals, acids, and bases. Compared to brass or stainless-steel ball valves, they have lower temperature and pressure resistance and lower mechanical strength. They are available with different piping connections, such as solvent sockets (glue connection), different flange types, or pipe threads. Double union, or true union valves, have separate pipe connection ends fixed to the valve body by a threaded connection. A true union ball valve with sockets and a manual handle is the most common. The valve can be easily removed for replacement, inspection, and cleaning. To learn more about these versatile valves read our ball valve introduction article.
Table of contents
- PVC properties
- Construction and design
- Polyvinyl Chloride production
- Selection criteria
- Applications
View our online selection of ball valves!
PVC properties
The list below provides a general overview of important characteristics of the material:
- Lightweight, durable, and long service life
- Recyclable and relatively low impact on the environment in comparison with other plastics
- No corrosion
- Resistant to many chemicals, acids, and bases
- Often used for sanitary applications, such as drinking water. PVC is an important material used to store or transfer food products.
- Most PVC ball valves up to DN50 have a maximum pressure rating of PN16 (16 bar at room temperature).
Construction and design
2-way
A 2-way PVC ball valve is a straight ball valve with 2 ports, an inlet, and an outlet. The media only flows in one direction in such valves, and they are considered inline with the rest of the assembly. These valves can be either open or closed. The valves quarter-turn feature makes it easier to use and to detect if the valve is open or closed. If the valves handle is parallel to the pipe or hose, the valve is open, and the media will flow from the inlet, through the balls bore, and out the outlet. If the handle is perpendicular to the pipe or hose, the valve is closed, and the media flow is shut off.
3-way
A 3-way PVC ball valve is the most commonly used multiport valve. This valve has 3 ports and has two design types: L-port and T-port. This refers to the bore design in the ball, which is the path of the media flow. The T-port or L-port allows the 3-way ball valve to mix, distribute, or divert the media flow. Therefore, understanding your bore design requirement is essential to ensure your desired media flow is possible as the ports can be in different positions. These 3-way manual valves are handle operated. Turning the handle a quarter turn will change the direction of the flow based on the valves bore design.
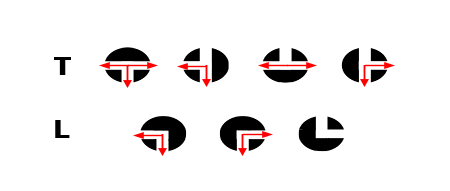
Figure 2: 3-way port design (T-Port and L-Port)
ISO-top
An electric or pneumatic actuator can drive the ISO- top PVC ball valves. These valves can be 2-way or 3-way and are great solutions to remotely control your valve. Typically, these valves have an ISO 5211 standard flange. Valves with an ISO-5211 flange are often referred to as "ISO-top." When selecting an actuator, it is important to check if the valve and actuator have the same flange size. Within the ISO 5211 standard, a range of flange sizes exists, such as F03, F04, F05, and F07. Another important parameter to select the right actuator is the operating torque of the valve. Please note that the exact values depend on multiple factors, such as medium type and pressure. Furthermore, values can vary between manufacturers.

Figure 3: PVC ball valve ISO-top
Polyvinyl Chloride production
PVC stands for PolyVinyl Chloride and is the third most used synthetic polymer after PE and PP. It is produced by the reaction of 57% chlorine gas and 43% ethylene gas. Chlorine gas is derived by electrolysis of seawater, and the distillation of crude oil obtains ethylene gas. In comparison to other plastics, PVC production requires significantly less crude oil (PE and PP require around 97% ethylene gas). Chlorine and ethylene react and form ethanedichlorine, which is then processed into a Vinylchlorine monomer. Furthermore, this material is polymerized to form PVC. Finally, some additives are used to alter properties such as hardness and elasticity. Because of the relatively simple production process and large availability of the raw materials, PVC is a cost-effective and relatively sustainable material compared to other plastics. PVC has a strong resistance against sunlight, chemicals, and oxidation from water.
What are U-PVC and C-PVC
U-PVC, or PVC-U, is an abbreviation of unplasticized Polyvinyl chloride. The material is also called rigid PVC. When PVC is mentioned as valve housing material, this is always unplasticized PVC. U-PVC doesnt contain phthalates; these are only used for flexible PVC.
CPVC, or chlorinated PVC, has a higher heat resistance and can be used for hot water. The chlorination of PVC obtains CPVC. An aqueous solution of PVC particles is chlorinated and exposed to UV light. The chlorine content is increased to 67 percent. CPVC is more expensive than regular PVC and is only used in niche applications, such as water heaters.
Selection criteria
The following selection criteria should be considered before selecting the PVC ball valve for your application:
- Bore design: The PVC ball valve can be straight 2-way or have a T- port or L-port 3-way bore design. For a straight flow, a 2-way valve is preferred. For applications like mixing, distributing, or diverting, a 3-way valve is used.
- Flow media: PVC valves are suitable for corrosive media like seawater, acids, bases, salt solutions, and organic solvents. However, PVC is not resistant to aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
- Temperature: PVC has a relatively low softening and melting point. It has a temperature range of -15 to 60°C.
- Pressure: PVC provides a low-pressure rating than brass or stainless steel valves.
- Cost: PVC ball valves are the most cost-effective alternative as compared to brass and stainless-steel ball valves.
To learn more about making the right selection of ball valve for your application, read our ball valve selection technical article!
Applications
PVC valves are used intensively in a wide range of commercial and residential applications. A list of typical markets where PVC ball valves are used includes:
- Domestic / Professional Irrigation
- Water treatment
- Water features and fountains
- Aquariums
- Landfills
- Swimming pools
- Chemical processing
- Food processing















