Air Compressor Ball Valves

Figure 1: Air compressor ball valve
Air compressors are a crucial part of operations in factories and workshops worldwide. Industrial air compressors are complex systems equipped with several components to guarantee optimal performance, and these units are the workhorses of a manufacturing plant. Valves used in air compressors provide a steady flow of compressed air for an extended period to meet the needs of various applications, including running pneumatic machinery in manufacturing plants. This article gives a detailed analysis of ball valves used in air compressors.
Table of contents
- What is an air compressor?
- Valves used in air compressors
- Ball valves for air compressors
- Air compressor ball valve design
- FAQs
View our online selection of ball valves!
What is an air compressor?
Compression is the process of forcing a confined volume of gas into a smaller space to increase its pressure. The process results in a rise in temperature and an increase in the stored internal energy of the gas. An air compressor is a pneumatic component that converts power into energy stored in compressed or pressurized air. An air compressor can also use a diesel or gasoline engine or an electric motor to force large quantities of air into a storage tank, increasing its pressure. Once the tank's pressure hits the designed upper limit, the air compressor shuts off automatically. The energy contained in compressed air facilitates various applications that utilize kinetic energy. Some of the typical applications of air compressors are:
- Inflation of tires
- Power multiple tools
- Spray painting
- Pressure washing
- Control water fountains
- Scuba diving
- Heating and cooling of engines
Valves used in air compressors
The common valves used in air compressors are the following:
Intake valve
The intake valve acts as the breathing port of an air compressor. It allows air to enter, which the valve then directs to the compressor head, where it is compressed to form compressed gas. Intake valves also control the loading and unloading of the air compressor and the size and flow of the air pressure.
Minimum pressure valve
The minimum pressure valve is located at the outlet just above the oil-gas separator. When using the minimum pressure, the valve acts as a buffer to control gas flow rate and prevent high-speed airflow damage. It has various components, including the valve core, valve body, and spring. It also features adjusting screws, sealing rings, and more.
Safety valve
A safety valve or overflow valve promises the compressor system's safety. If the system pressure exceeds the specified value, the safety valve discharges some gas into the atmosphere to ensure the system doesn't trigger accidents because of excessive pressure.
Temperature control valve
The temperature control valve controls the lubricating oil entering the oil cooler to ensure the rotor temperature is within the desired level.
Oil stop valve
The oil stop valve or oil cut valve is a switch that controls oil paths into screw heads. The valve stops the oil supply to the main engine once the compressor is turned off. This ensures the lubricating oil doesn't spray out of the main engine port.
Check valve
A check valve, or a one-way valve, prevents compressed oil and gas mixture from back injection into the main engine whenever the machine shuts down.
Compressed air pressure regulating valve
Ideally, different pneumatic tools require varying pressure levels. The air pressure regulating valve allows to adjust the settings to guarantee the right air pressure. Without the regulating valve, it becomes pretty hard to adapt and control the pressure and intensity of the air flowing from the compressor tank into the pneumatic tool.
Ball valves for air compressors
Solenoid valves and ball valves are commonly used in compressed air systems. A ball valve is a shut-off valve that controls fluid flow through a rotating ball with a bore. The valve allows or prevents the flow of liquids or gases in a piping assembly by rotating the ball that has a bore inside.
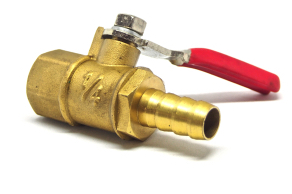
Figure 2: Ball valve
Ball valves are typically used at two locations within an air compressor:
- Inlet valve: An inlet valve regulates the amount of air sucked in by the air compressor to fill the cylinder. The inlet valve closes when the desired air pressure is reached within the compressor. Thus no more air can be taken in and compressed when the desired pressure level is reached.
- Outlet valve: An outlet valve or unloader valve controls the flow of compressed air at the output acting as an air release valve.
The ball valves can be operated manually by rotating the lever or actuated electrically. In automated systems, the ball valve can be activated by a timer to switch the compressed air system on and off at regular intervals. The valve is typically open during the day and closed at night. This is an efficient way to prevent the loss of valuable compressed air.
Ball valves used for inlet and outlet are either completely open or completely closed. Solenoid valves are typically used for modulating operations where the compressor works at any point between 0 and 100 percent. Read our article on compressed air valves for more information.
Air compressor ball valves also come in various designs and features to meet various industrial needs. The standard and specifications for ball valves can vary from one industry to another. Some of the common types of ball valves for air compressors include:
- Full port ball valve: This valve features an oversized hole in the ball that is the same size as the pipeline. When you choose a full port ball valve, it ensures lower friction loss and unrestricted flow.
- A trunnion ball valve: This valve has a mechanical means of anchoring the ball at the top and bottom. This design is also ideal for larger and higher pressure valves. Read our article on trunnion ball valves for more details.
- A v-port ball valve: Features a v-shaped ball or a v-shaped seat. This design ensures the orifice opens and closes in a more controlled manner with a closer to linear flow characteristic.
- Standard port ball valve: A standard port ball valve valve has a smaller ball and a correspondingly smaller port. Flow-through this valve is one pipe size smaller than the valve's, resulting in slightly restricted flow.

Figure 3: Ball valves used in an air compressor
Air compressor ball valve design
As the ball valves employed in an air compressor deal with air as the medium, it is crucial to select the materials compliant with air for the various parts of the valve like the valve body, stem, and seal. Read our article on the chemical resistance of materials for more details on the compliance of each valve material with the different media used. A few options for air ball valves are:
- Valve housing: The valve housing contains all the internal components of a ball valve. The housing is a stiff and rigid material, which could be thermoplastic lined metal, metal like stainless steel, alloys like brass, or PVC to guarantee the ultimate protection of components.
- Seal: Seal materials that can be used for compressed air are FKM (Viton), PTFE, or NBR. EPDM is less suitable because compressed air often contains oil.
- Stem: The usual choice for stems is stainless steel for coated carbon steel or cast iron bodies.
FAQs
What is the ball valve on an air compressor?
Ball valves control airflow in an air compressor and function as an inlet or outlet valves.
Can ball valves be used for air?
Ball valves control various media, including air, water, gas, and other media. These ball valves are also useful for operations that require perfect shutdown.
Are all air compressor ball valves the same?
Ball valves in an air compressor differ depending on the application. There are sometimes up to 5 valves on a single compressor performing different functions.









