BSP - British Standard Pipe
BSP threads are 55 ° V-threads with rounded roots and crests, as seen in Figure 1. Though they are used internationally, there are numerous global thread standards that are more common in other countries, like the United States (NPT), Canada, (NPT), China (GB), etc. BSP, British Standard Pipe, threads have a pipe thread major diameter that is slightly smaller than the actual OD (outer diameter) of the pipe, and the minor diameter will be very close to (smaller than) the inside diameter of the female thread. There are two types of BSP threads:
- BSPP: Both the male and female threads are parallel. BSPP connections are widely used in the UK, Europe, Asia, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. Table 1 shows the dimensions of the BSPP standard.
- BSPT: The male threads are tapered, and the female threads are commonly parallel. BSPT connections are especially popular in China and Japan. Table 2 shows the dimensions of the BSPT standard.
Read our thread design article for more details on the various thread design parameters.
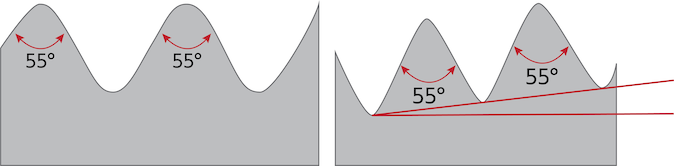
Figure 1: A BSPP male parallel thread profile (left) and a BSPT tapered male thread profile (right)
How to identify a BSP thread
First, find the thread’s inner diameter to determine the threads per inch count for the BSPT fittings. Use a vernier caliper to take a reading from inside the bore of the fitting. Then, check the bore size with thread pitch and threads per inch given in Tables 1-3 to find the desired size and its related specifications. Read our article on measuring threads for more details on using a vernier caliper to measure the thread diameter.
Click the button below to download the following BSP thread charts.
Table 1: BSPP (G) – British Standard Pipe Parallel
| Nominal Thread Size | Major Diameter (mm) | Minor Diameter (mm) | TPI (in-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G 1/16 | 7.723 | 6.561 | 28 |
| G 1/8 | 9.728 | 8.566 | 28 |
| G 1/4 | 13.157 | 11.445 | 19 |
| G 3/8 | 16.662 | 14.950 | 19 |
| G 1/2 | 20.955 | 18.631 | 14 |
| G 3/4 | 26.441 | 24.117 | 14 |
| G 1 | 33.249 | 30.291 | 11 |
| G 1 1/4 | 41.910 | 38.952 | 11 |
| G 1 1/2 | 47.803 | 44.845 | 11 |
| G 2 | 59.614 | 56.656 | 11 |
| G 2 1/2 | 75.184 | 72.226 | 11 |
| G 3 | 87.884 | 84.962 | 11 |
Table 2: BSPT (R/Rp) – British Standard Pipe Tapered
| Nominal Male Tapered Thread Size (inch) | Nominal Female Parallel Thread Size (inch) | Major Diameter (mm) | Minor Female Diameter (mm) | TPI (in-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R 1/16 | RP 1/16 | 7.723 | 6.490 | 28 |
| R 1/8 | RP 1/8 | 9.728 | 8.495 | 28 |
| R 1/4 | Rp 1/4 | 13.157 | 11.341 | 19 |
| R 3/8 | Rp 3/8 | 16.662 | 14.846 | 19 |
| R 1/2 | Rp 1/2 | 20.955 | 18.489 | 14 |
| R 3/4 | Rp 3/4 | 26.441 | 23.975 | 14 |
| R 1 | Rp 1 | 33.249 | 30.111 | 11 |
| R 2 | Rp 2 | 59.614 | 56.476 | 11 |
Table 3: British Standard Pipe dimensions for standard thread sizes
Nominal G / R size (in) |
Corresponding Pipe |
||
| DN (mm) | Actual OD (mm) | Wall (mm) | |
| 1/16 | 3 | ||
| 1/8 | 6 | 10.2 | 2 |
| 1/4 | 8 | 13.5 | 2.3 |
| 3/8 | 10 | 17.2 | 2.3 |
| 1/2 | 15 | 21.3 | 2.6 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 26.9 | 2.6 |
| 1 | 25 | 33.7 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 50 | 60.3 | 3.6 |
Labeling
BSP threads are identified with letters, each of which represents the type of thread and their associated standards:
- G: external and internal parallel (ISO 228) - BSPP
- R: external taper (ISO 7, EN 10226, BS 21, DIN 2999, JIS B 0203) - BSPT
- Rp: Internal parallel (ISO 7-1, EN 10226) - BSPT
- Rc: internal taper (ISO 7) - BSPT
-
Rs:external parallel (BS 21) - BSPT- Obsolete
- ISO 7: Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads.
- ISO 228: Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are not made on the threads.
Example
EN 10226 Rp 2 ½: This refers to a British Standard Pipe thread tapered (EN 10226) with an internal parallel form (Rp) and a nominal size of 2 ½ inches.
BSP vs NPT
NPT/NPS threads have a 60° angle and have flattened valleys and peaks, whereas BSP threads have a 55° angle and have rounded peaks and valleys. NPT/NPS and BSP threads are incompatible due to the differences in their thread forms. Table 4 summarizes NPT and BSP standards’ threads per inch.
Table 4: NPT vs BSP threads per inch (TPI)
Thread size |
Pitch (Threads per inch) |
|
| NPT/NPS | BSP | |
| 1/8 | 27 | 28 |
| 1/4 | 18 | 19 |
| 3/8 | 18 | 19 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 14 |
| 1 | 11 1/2 | 11 |
| 1 1/4 | 11 1/2 | 11 |
| 1 1/2 | 11 1/2 | 11 |
| 2 | 11 1/2 | 11 |
| 2 1/2 | 8 | 11 |
| 3 | 8 | 11 |
| 3 1/2 | 8 | 11 |
| 4 | 8 | 11 |
| 5 | 8 | 11 |
| 6 | 8 | 11 |
Read our NPT, Unified thread standard, and M-Metric thread standards for more information on other thread standards.
FAQs
What is a BSP thread?
BSP thread is a standard for pipe threads used globally, featuring BSPP (parallel) and BSPT (tapered) types for sealing and connecting pipes and fittings in plumbing and gas systems.
What is the difference between NPT and BSP threads?
NPT threads have a 60° angle and are tapered, while BSP threads have a 55° angle and can be parallel or tapered.











