Pneumatic Systems - Glossary
Figure 1: Pneumatic systems play an integral role in many different processes.
This glossary serves as a reference for terms related to pneumatic systems, providing clear and succinct definitions for a wide array of components, measurements, and concepts integral to these systems. Pneumatic systems, which use compressed air to perform work, are employed across various industries, from manufacturing to robotics.
| Term | Definition |
| Actuator | A pneumatic actuator (e.g., rack and pinion) is a device that converts energy from compressed air into mechanical motion. |
| After cooler | A heat exchanger that cools air leaving the compressor to condense moisture. |
| Air motor | A motor powered by compressed air rather than electricity, e.g., a vane motor. |

Figure 2: An air vane motor.
| Air, free | Air at atmospheric conditions at any specific location. |
| Air, standard | Dry air at 20°C (68°F), 101.3 kPa (14.7 psi) and 0% relative humidity. |
| Automatic drain | An automatic drain is a device that automatically removes condensate from the air system. |

Figure 3: A float operated automatic drain valve
| Bar | A unit of pressure, equal to 100,000 pascals or approximately atmospheric pressure at sea level. |
| Bore size | The internal diameter of a cylinder. |
| Check valve | A check valve in a pneumatic system allows flow in one direction and prevents backflow. |

Figure 4: A brass check valve
| Compressor | A machine that increases the pressure of air by reducing its volume. |
| Compressed air | Air that is at a higher pressure than atmospheric pressure. |
| Cracking pressure | The pressure at which a valve begins to open. |
| Cushioning | Cushioning is a technique used in pneumatic cylinders to slow down the piston at the end of its stroke to prevent impact. |
| Cylinder | A pneumatic cylinder is a device that converts compressed air into mechanical energy through linear motion. |

Figure 5: A pneumatic cylinder
| Cylinder cap | The closed end of a cylinder where the piston rod does not emerge. |
| Cv | Cv is a measure of the flow capacity of a valve. |
| Dew point | The temperature at which air is saturated with moisture and condensation begins. |
| Double acting cylinder | A double acting cylinder uses air pressure to move the piston in both directions. |
| FRL (Filter, Regulator, Lubricator) | An FRL is a combination unit that prepares compressed air for use in pneumatic systems. |

Figure 6: An FRL unit
| Filter | A device that removes particulates and contaminants from air. |
| Kv | Similar to Cv but in metric units, Kv indicates the flow rate of water in cubic meters per hour at a pressure drop of one bar. |
| Manifold | A pneumatic manifold has multiple ports for distributing or collecting air to/from different lines. |

Figure 7: A pneumatic manifold
| Muffler | Also called a silencer, a muffler is a device that reduces the noise created by the exhaust of pressurized air. |
| Non-return valve | Another term for a check valve; it allows flow in one direction only. |
| Packing | Sealing material used to prevent leaks in pneumatic systems. |
| Pascal | A unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one newton per square meter. |
| Pneumatic gripper | A pneumatic gripper is a pick-and-place device that uses compressed air to operate gripper jaws, also called fingers. These fingers, similar to human fingers, help in grasping, holding and releasing the work pieces. |
| Poppet valve | A valve consisting of a hole and a tapered plug, usually operated by a solenoid. |
| Port | An opening in a cylinder or valve where air enters or exits. |
| Pressure, absolute | The total pressure within a system, including atmospheric pressure. |
| Pressure, atmospheric | The pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere, approximately 101.3 kPa at sea level. |
| Pressure, gauge | The pressure of a system above atmospheric pressure. |
| Pressure, relative | The difference between the absolute pressure and the atmospheric pressure. |
| Relative humidity | The amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at that temperature. |
| Rodless cylinder | A cylinder where the piston moves within the cylinder without an external rod. |
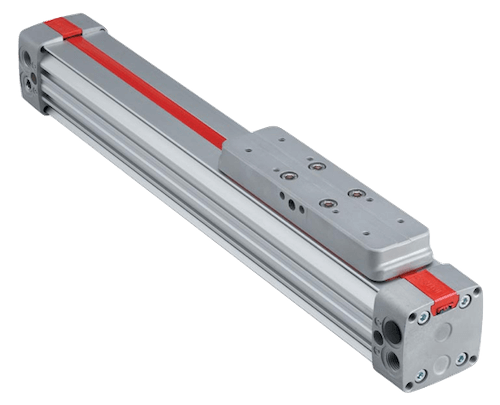

Figure 8: A rodless cylinder
| Silencer | Also called a muffler, a silencer is a device that reduces the noise created by the exhaust of pressurized air. |

Figure 9: A cone shaped and flat pneumatic cylinder
| Single acting cylinder | A cylinder where air pressure is applied to only one side of the piston, causing movement in one direction only. |
| Slide unit | A device that allows for linear movement in a pneumatic system. |
| Solenoid valve | A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve controlled by an electric current. |
| Vacuum | A condition where the pressure is below atmospheric pressure. |

Figure 10: 5/2-way pneumatic solenoid valve




