Pneumatic Muffler Throttle Valves

Figure 1: Pneumatic muffler throttle valves
A pneumatic muffler throttle valve combines the functions of a muffler and a throttle valve into a single unit. The primary purpose is to vent pressurized air from a pneumatic system to the atmosphere while controlling the flow rate and reducing the noise generated by the exhaust air. The muffler component decreases the audible noise by increasing the surface area through which the air is released, thereby protecting workers' hearing and meeting application noise specifications. The throttle valve component allows for precise control over the exhaust airflow, thereby controlling the performance of the pneumatic system, such as the speed of a pneumatic cylinder's piston. The valve also provides protection against the entry of debris, particles, or liquids into the exhaust ports.
Note: The terms pneumatic muffler and pneumatic silencer are used interchangeably in this article. In addition, a pneumatic muffler throttle valve is also commonly referred to as an adjustable pneumatic silencer or flow control silencer.
Table of contents
- Design
- Working mechanism
- Selection criteria
- Installation
- Pneumatic muffler throttle valve applications
- Maintenance
View our online selection of muffler throttle valves!
Design
The design of a muffler throttle valve in a pneumatic system typically includes:
- Housing: Made of materials like brass or stainless steel, the housing contains the throttle mechanism and the porous exhaust port.
- Throttle mechanism: An adjustable knob, usually a needle valve, that allows for the regulation of exhaust airflow. The throttle valve can also have other adjustment mechanisms like a locknut or knurled screw.
- Porous exhaust port: Disperses the exhaust air over a larger area to reduce noise.
- Connection port: Usually features threads for easy installation into a pneumatic system.
- Perforations or porous material: Prevents contaminants from entering the system while allowing exhaust airflow.
Read our pneumatic muffler article for more details on the design, specifications, and applications of pneumatic mufflers.
Working mechanism
By turning the knob or screw on the throttle mechanism, the user can adjust the flow rate of the exhaust air, which affects both the noise level and the speed of air exhaustion. The position of the screw will increase or decrease the size of the valve orifice and thus adjust the flowrate of the air exiting the valve. The porous exhaust port disperses the exhaust air over a larger surface area, reducing the noise generated by the rapid release of compressed air. Additionally, the throttle valve component allows for precise control over the exhaust airflow, enabling quick and easy modifications to meet specific application requirements.
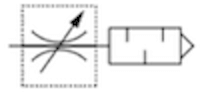
Figure 2: Pneumatic muffler throttle valve symbol
Selection criteria
When selecting a pneumatic silencer throttle valve, it is essential to consider various parameters to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- Connection size: Ensure the connection size of the valve matches the size of the ports in the pneumatic system. Common sizes include ⅛ inch, ⅜ inch, ½ inch, ¾ inch, and 1 inch.
- Connection type: Identify the type of threading required for the system, such as BSP (British Standard Pipe) or NPT (National Pipe Taper), to ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
- Material: Choose a material that is compatible with the operating environment and the media being used, such as brass, stainless steel, or polymer to ensure durability and resistance to corrosion and wear. Brass is ideal for general-purpose applications due to its corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Stainless steel is suitable for harsh or corrosive environments due to its high corrosion resistance and strength. Polymer-based muffler throttle valves, made from polyethylene (PE) or polyamide (PA), are lightweight, oil and moisture-resistant, and ideal for low-pressure, low-temperature applications. Read our chemical resistance guide for more information on the compatibility of various materials with different media.
- Length: Sound absorber length is the length protruding when the muffler is fully installed. Ensure the muffler throttle valve fits within the available space and meets the noise reduction and flow rate requirements. Longer mufflers generally offer better noise reduction but may slightly reduce flow rate and be more challenging to install in tight spaces. Muffler lengths like 20mm, 25mm, and 30mm are commonly available.
Installation
The installation process for a pneumatic silencer throttle valve involves the following steps:
- Identify the exhaust port: Locate the exhaust port on the pneumatic component.
- Prepare the threads: Ensure the threads on both the exhaust port and the muffler throttle valve are clean and free of debris. Apply thread sealant or Teflon tape to the valve if needed.
- Screw in the muffler throttle valve: Carefully screw the valve into the exhaust port by hand to avoid cross-threading. Once hand-tight, use a wrench to tighten securely, but do not overtighten.
- Adjustment mechanism: After installation, rotate the knob to set the desired flow rate.
- Test the system: Test the pneumatic system to ensure the valve functions correctly. Check for leaks and verify noise reduction and flow control.
Pneumatic muffler throttle valve applications
Muffler throttle valves are typically installed at the exhaust ports of various pneumatic components:
- Pneumatic cylinders and actuators: To control piston speed, manage return speeds, and reduce noise. For example, by controlling the exhaust speed of a pneumatic cylinder one can control how quickly the piston is able to extend and/or retract.
- Pneumatic valves: To regulate exhaust airflow and reduce noise.
- Pneumatic tools: To control exhaust airflow and enhance operator comfort.
- Air preparation units: To manage exhaust airflow from filters, regulators, and lubricators.
Determining whether an application requires a pneumatic silencer or a pneumatic silencer throttle valve depends on the specific needs of the system. If the primary concern is reducing noise from exhaust air without needing to control the flow rate, a standard pneumatic silencer will suffice. However, if precise control over the exhaust airflow is necessary to regulate the speed of pneumatic components, such as cylinders or actuators, while also reducing noise, a pneumatic silencer throttle valve is the appropriate choice. Read our article on Festo's pneumatic muffler throttle valves for more information on these devices.
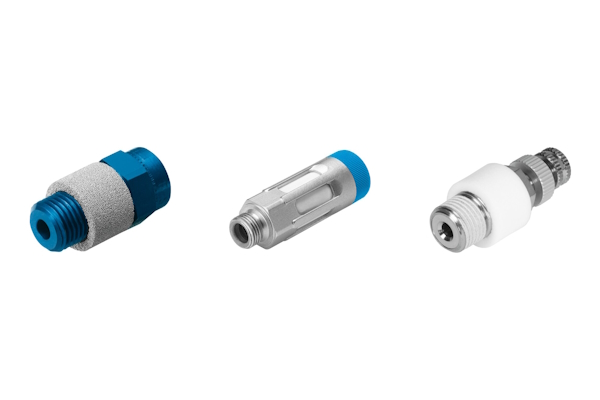

Figure 3: Festo's pneumatic muffler throttle valves series: GRU (left), GRE (middle), and VFFK (right).
Maintenance
Maintenance of a pneumatic muffler throttle valve involves:
- Regular cleaning: Depending on usage, incorporate a silencer cleaning schedule into the system maintenance planning. Remove the silencer and rinse it under lukewarm tap water. Use compressed air to blow away any remaining dirt particles from outside to inside.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the throttle mechanism and porous exhaust port for signs of wear or clogging.
- Replacement: Replace the muffler throttle valve if it shows signs of significant wear or if the noise reduction and flow control capabilities are compromised.





